FoodieNet - Food Image Classification Model
This project focused on developing a deep learning model for food image classification, with a novel approach to handling fine-grained visual categorization challenges in food recognition. The goal was to improve classification accuracy by effectively capturing subtle visual differences between similar food categories.
Project Overview
- Duration: 4 months
- Role: Team member in a 4-person research project
- Technologies: PyTorch, ResNet-50, Vision Transformer
Problem Statement and Approach
Food image classification presents unique challenges due to the fine-grained nature of food categories and high intra-class variations. Our approach focused on developing a novel architecture that could better capture subtle visual differences while maintaining computational efficiency.
Technical Implementation
-
Model Architecture:
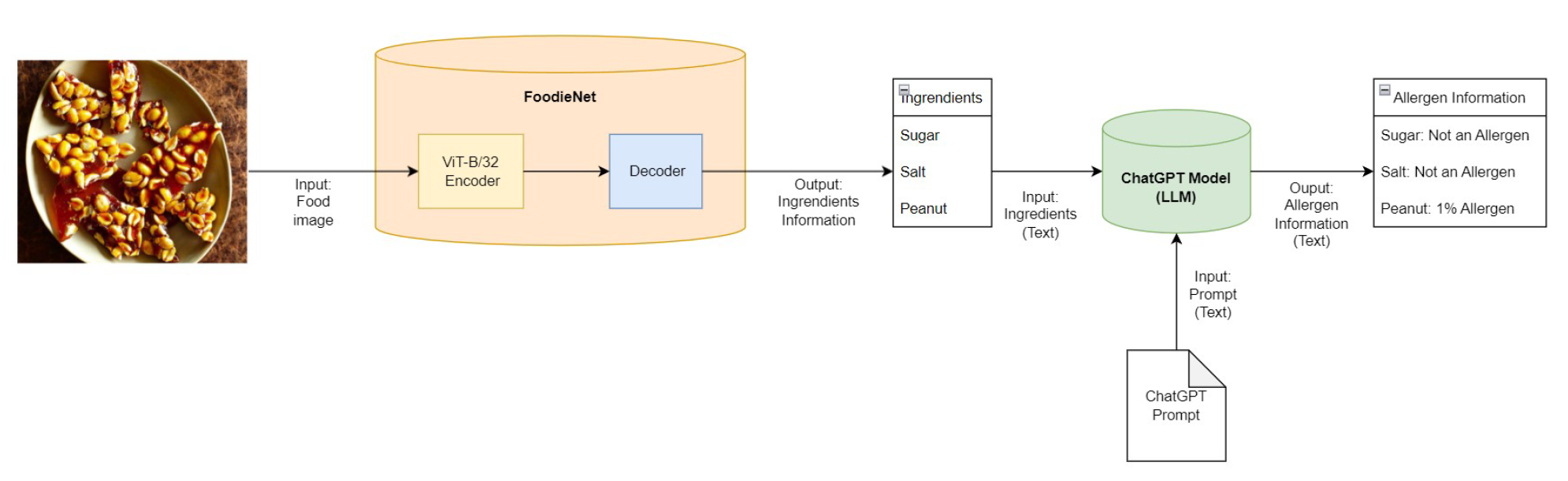 FoodieNet Architecture: End-to-end pipeline for food image classification and ingredient/allergen analysis
FoodieNet Architecture: End-to-end pipeline for food image classification and ingredient/allergen analysis- Developed FoodieNet, combining CNN and Transformer architectures
- Utilized ResNet-50 as the backbone network
- Implemented a novel attention mechanism for fine-grained feature extraction
- Designed a hybrid architecture leveraging both local and global features
- Integrated with LLM for ingredient and allergen information extraction
- Key Components:
- Multi-scale feature extraction
- Attention-based feature refinement
- Hierarchical feature fusion
- Category-specific feature enhancement
- Training Strategy:
- Implemented progressive training approach
- Utilized data augmentation techniques
- Applied transfer learning from ImageNet pre-trained models
- Employed mixed precision training for efficiency
Results and Impact
- Achieved 87.2% top-1 accuracy on Food-101 dataset
- Demonstrated 2.1% improvement over baseline ResNet-50
- Reduced computational complexity compared to pure transformer approaches
- Successfully handled fine-grained classification challenges in food recognition
Key Findings
- Architecture Benefits:
- Hybrid approach effectively captured both local and global features
- Attention mechanism improved discrimination between similar food categories
- Multi-scale feature extraction enhanced model robustness
- Performance Analysis:
- Strong performance on visually similar food categories
- Effective handling of intra-class variations
- Computational efficiency suitable for practical applications
This project demonstrated the effectiveness of combining traditional CNN architectures with modern attention mechanisms for fine-grained visual classification tasks. The resulting model showed significant improvements in food image classification while maintaining practical computational requirements.
